#CGM
#A CGM for Christmas 2024
Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) from an IT Perspective.
Contact Us to get your today!
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) is a revolutionary technology in healthcare that has greatly impacted the lives of people managing diabetes. From an IT standpoint, CGM systems integrate health, data, and technology to provide real-time glucose monitoring, aiding in more effective management of diabetes. Let’s explore the components, IT infrastructure, and challenges associated with CGM technology.
1. Overview of CGM Technology
CGM devices continuously measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid, providing real-time feedback on blood sugar fluctuations. Typically, a small sensor is inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels. The sensor sends this data wirelessly to a receiver, smartphone, or wearable device. Advanced CGM systems can even integrate with insulin pumps to automate insulin delivery based on the user’s glucose levels.
From an IT perspective, this involves complex data collection, processing, and secure transmission between devices. The integration of hardware (sensors, receivers) with software (mobile apps, cloud systems) is key to ensuring seamless user experiences.
2. Data Collection and Management
At the core of CGM is data collection. CGM systems generate vast amounts of data that need to be captured, processed, and stored securely. Data collected by the sensors is transferred to cloud-based platforms or local storage on devices. These systems offer:
- Real-time data synchronization: Continuous and accurate glucose readings.
- Cloud integration: Many CGM platforms store data in the cloud, allowing for remote monitoring by healthcare providers and easy access for users.
- Data analytics: CGM platforms leverage analytics to predict glucose trends, generate insights, and trigger alerts for low or high glucose levels. These insights are often visualized on dashboards, helping users and healthcare professionals make informed decisions.
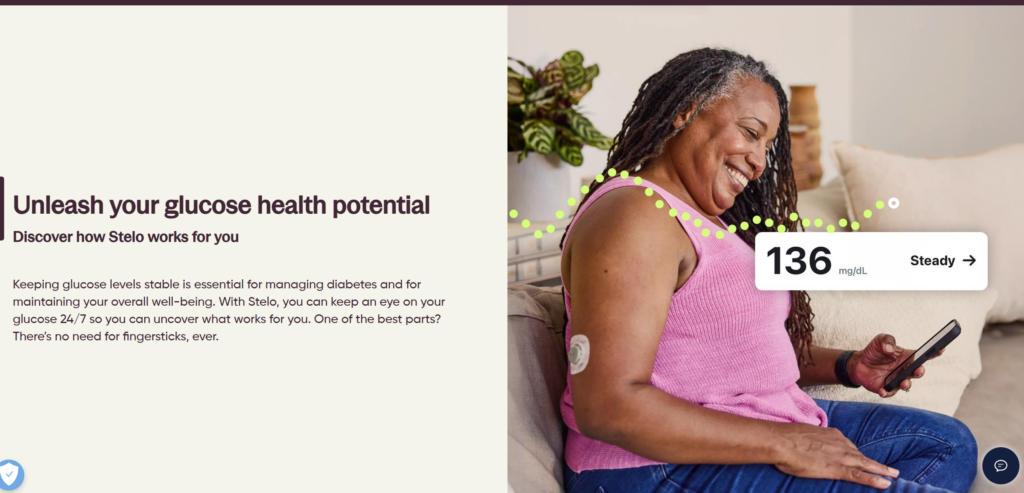
3. Connectivity and Integration with Other Devices
The ability of CGM devices to communicate with smartphones, smartwatches, and insulin pumps through Bluetooth or Wi-Fi demonstrates the importance of connectivity in healthcare technology. IT professionals need to ensure that these devices remain interconnected reliably and securely. Data must flow seamlessly from the sensor to the receiving device without latency or loss of information. Moreover, integration with insulin pumps or fitness trackers creates a more holistic view of the user’s health.
4. Security and Privacy Concerns
CGM systems, like all medical devices, handle sensitive health data, making data security a critical concern. Since CGM devices collect and transmit personal health information (PHI), they are subject to strict regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States. IT teams must ensure:
- Encryption: All data transmitted between devices should be encrypted to prevent unauthorized access.
- Authentication: Strong authentication protocols should be implemented to ensure that only authorized users can access CGM data.
- Compliance: IT infrastructure supporting CGM must comply with relevant data privacy laws to protect patient information.
5. Challenges and Opportunities
Although CGM technology has advanced rapidly, there are still challenges from an IT perspective, including:
- Interoperability: Integrating CGM data with other health systems like Electronic Health Records (EHRs) or third-party apps can be difficult due to varying standards and protocols.
- Latency: Ensuring real-time data transfer without delays is essential for accurate monitoring and timely interventions.
- Data overload: Users and healthcare providers may be overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data generated, making effective data management and filtering critical.
However, there are also numerous opportunities for growth:
- AI and Predictive Analytics: As CGM systems generate large datasets, there’s a potential for using machine learning to predict glucose trends and suggest proactive interventions.
- Telehealth integration: CGM platforms can be integrated with telehealth services, allowing healthcare providers to remotely monitor patients and adjust treatment plans based on real-time data.
6. The Future of CGM and IT
The evolution of CGM technology is closely tied to advancements in IT infrastructure, cloud computing, and AI. As CGM devices become more prevalent, IT professionals will play a critical role in:
- Enhancing connectivity: Developing faster, more secure, and reliable networks for real-time data transmission.
- Improving user experience: Creating intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that present actionable insights from CGM data.
- Ensuring scalability: With growing user bases, IT infrastructures must be designed to scale, handling larger volumes of data without compromising performance or security.
Conclusion
CGM is not just a medical innovation; it’s a data-driven solution that bridges healthcare and technology. From managing complex data streams to ensuring security and integration, the role of IT in CGM systems is foundational. As CGM technology continues to advance, it will require even more sophisticated IT infrastructures to support the growing demands of users and healthcare professionals.